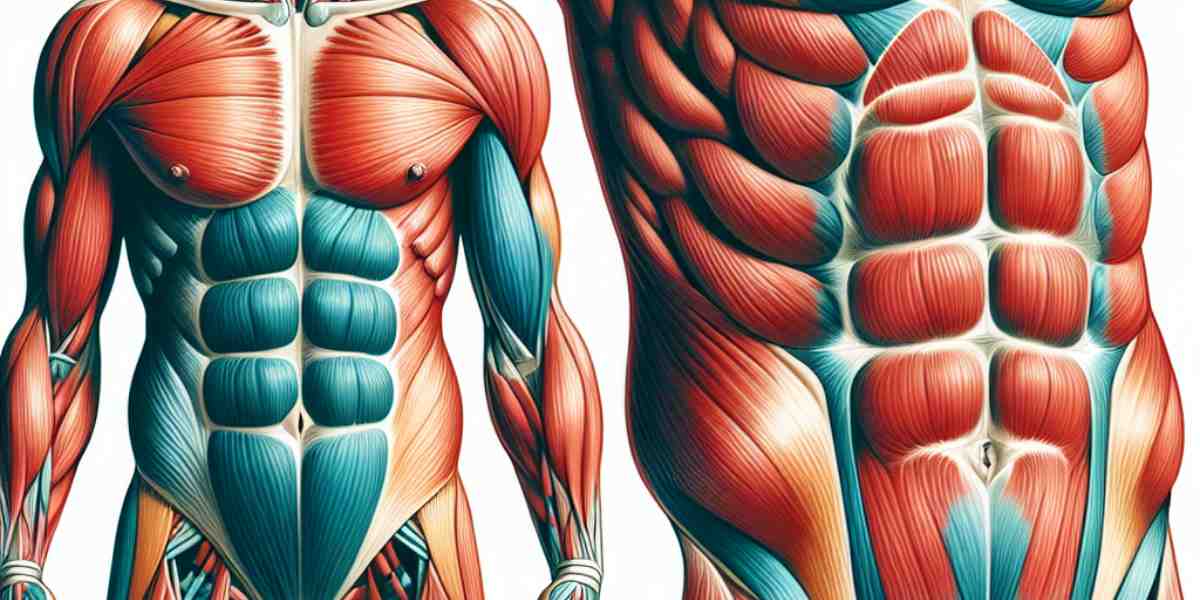
The abdominal muscles, or “abs”, are a group of four muscles located in the front and sides of the abdomen. They are responsible for flexing the trunk, stabilizing the spine, and aiding in respiratory function. They can also be involved in a few actions of the upper extremities.
The abdominal muscles are the largest in the body and are composed of a transverse and two oblique segments. The rectus abdominus is the most superficial of the abdominal muscles and is involved in trunk flexion and spinal stabilization. The rectus abdominus is what gives you that “six-pack” look if it’s well-defined.
The other three muscles of the abdominal group are known as the internal and external oblique muscles. These muscles are responsible for torso rotation, spinal stabilization, and hip flexion. The two oblique muscles also assist in respiration by compressing the rib cage.
The Ab muscles are part of what often is referred to as the “core” muscle.
Contents
What Are The Function of The Abdominal Muscle?
The rectus abdominis is a long, flat muscle located in the front of the abdomen. It is commonly referred to as the “six-pack muscle” because of its distinctive appearance. The rectus abdominis has several important functions, including:
- Providing support for the spine – The rectus abdominis helps to stabilize the spine and pelvis, which is especially important during activities such as lifting or running.
- Aiding in breathing – The rectus abdominis assists in the breathing process by contracting and relaxing to help move air in and out of the lungs.
- Assisting in movement – The rectus abdominis aids in movements such as bending forward or twisting at the waist.
The external oblique is a large, flat muscle that covers the sides and front of the abdomen. It has several important functions, including:
- Core stabilization: The external oblique helps to stabilize the spine and pelvis, which is essential for proper movement and posture.
- Movement: The external oblique aids in movements of the trunk, such as bending and twisting.
- Muscle balance: The external oblique works with other muscles in the abdominal region to maintain balance and stability.
- Anatomical landmark: The external oblique is an important anatomical landmark for identifying other structures in the abdominal region.
The internal oblique is part of the muscular anatomy of the abdominal wall. It is located under the external oblique muscle and runs at a diagonal angle from the lower ribs to the pelvis. The internal oblique has several functions, including assisting in core stabilization and aiding in the movements of the trunk.
The internal oblique assists in core stabilization by helping to maintain balance and preventing excessive movement of the spine. It also aids in movements of the trunk, such as bending and twisting. The internal oblique is an important muscle for overall health and well-being.
The internal oblique is made up of three main muscle groups: right crus, left crus, and central tendon.
The transverse abdominis is a key player in the function of the core. This muscle extends from the lower ribs to the pelvis and acts to stabilize the spine and pelvis. The transverse abdominis is the deepest layer of abdominal muscles and works to compress the abdominal contents.
This muscle is particularly important for stabilizing the spine during movements such as lifting or twisting. It also helps to control breathing by regulating pressure on the abdominal organs. The transverse abdominis is essential for maintaining a strong, healthy core.
Why You Should Strengthen Your Abs Muscle
Most people believe that abs are purely for show and that the only way to work them is by doing sit-ups or Crunches. However, the abs do much more than give you a six-pack. This muscle group is responsible for stabilization, posture, and balance, and strengthening them can have a profound impact on your overall health and quality of life.
The benefits of strong abs include:
Improve your Posture.
Having strong abs can help improve your posture by keeping your spine in alignment. This is especially important if you sit at a desk all day or spend a lot of time hunched over your phone. Strong abs will help you sit up straighter and stand taller.
Prevent Injuries.
Having strong abdominal muscles can also help prevent injuries. Your core helps stabilize your body, and weak core muscles can lead to pain in the lower back and hips. By strengthening your abs, you’ll be less likely to experience these types of injuries.
How to Get Started Strengthening Your Abs
Many different exercises can help strengthen your abs, but one of the most effective is the plank. The plank is a simple but challenging move that targets all of the muscles in your core, including your rectus abdominis. To do a plank, simply get into a push-up position and hold yourself up with your forearms instead of your hands.
Keep holding until your body shivers, and you begin to lose your tight posture.